A bruise (also known as a contusion or hematoma) occurs when a blow causes the blood vessels close to your skin’s surface to tear. This causes blood to ooze out of these blood vessels allowing the contents to leak into the soft tissue under your skin. As a result, a bruise is recognized as a discoloration of your skin. The blood trapped beneath your skin allows the affected skin to appear black and blue.
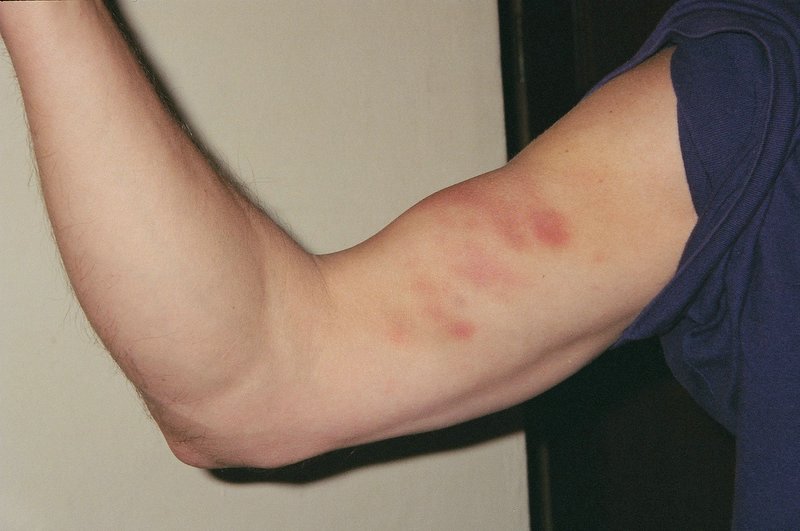
Bruises are classified into three types:
- Subcutaneous bruise: Bruises beneath the skin
- Intramuscular bruise: Within an underlying muscle
- Periosteal: Bruises in the bone (most severe)
Causes
- You are susceptible to bruises if you take blood thinning medications such as aspirin or warfarin
- Sports injuries
- Falls
- Automobile accidents
- Physical assault
Symptoms
- Pain
- Swelling
- Skin discoloration (color changes from purple to greenish brown after which normal skin color is recovered)
Treatment
Things to remember:
- Do not pierce the bruise using a needle to drain the blood out
- Do not continue running or playing using the bruised part of your body if it hurts a lot
- Do not try to ignore the swelling and pain
Call for medical help, if:
- The bruised part covers a large area of your body and you feel extreme pressure and pain on the affected area. The pressure may be due to a condition called compartment syndrome which results due to extreme pressure on the soft tissue and other contents lying beneath your skin. This can drastically reduce the oxygen supply to these tissues which can lead to severe, life threatening problems if prompt help is not sought.
- Bruises appear on your body without any possible cause such as injury, accident or fall.
- The bruised area is showing signs of infection such as pus, fever, drainage of any form of liquid or red streaks.
- Abnormal bleeding starts from other, unaffected parts of your body such as your gums, nose, eyes, and mouth or in your stool or urine.
First aid
- Wrap some ice with a clean piece of cloth and place it on the affected area to reduce swelling and pain. Do NOT directly place bare ice on the skin as this may lower the body temperature and lead to shock. Apply pressure using the wrapped ice for 15 minutes per hour.
- If it is possible, elevate the bruised area above heart level as this may allow blood to flow with the help of gravity.
- Allow the affected part of your body to rest and do not try to overwork it.
- If prescribed by the doctor, take acetaminophen in case of severe pain. Do NOT take aspirin or ibuprofen as they may aggravate the condition.
If you feel increased pressure on your wound, it may be due to compartment syndrome. Call for prompt medical help immediately as surgery will be needed to reduce the pressure build up.
Prevention
- Wear seatbelts when you are riding in vehicles
- Teach children safety precautions
- Stay safe and try to be careful and less clumsy around the house to prevent falls and accidents
- Wear padded safety equipment while engaging in sports activities
Managing Bruising with First Aid
To learn to recognize and manage basic first aid situations such as bruising and other injuries take a St Mark James training class with a provider near you. Check out the top Canadian providers here.
Related Video to Bruising for Children
